Overview
The U.S. leads the global healthcare industry with an annual spending of USD 3,649.4 billon in the year 2018. With advanced diagnostics, drugs and treatments, the U.S. has been historically known for its sophisticated healthcare services. These modern technologies and their implementations, however, have significantly impacted the costs of treatment thereby turning this basic need into a luxury across the country. According to the National Health Expenditures (NHE), an American citizen, on an average, spends over USD 11,172 as of year 2018 per year over healthcare services, which is quite huge as compared to some of the other nations across the globe.
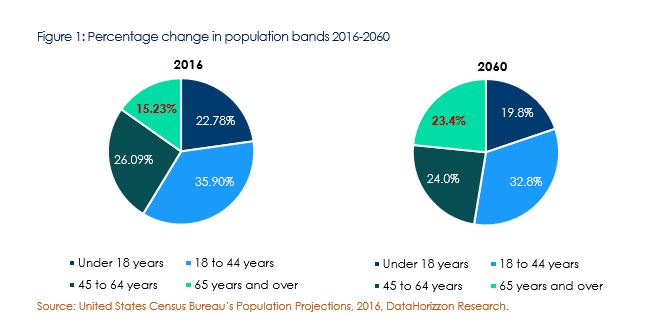
Nonetheless, the healthcare industry in the U.S. is expected to witness steady growth over the next eight years. This growth is majorly attributed to the ageing population in the U.S. In the year 2016, 15.23% of the entire nations’ population was observed to be in the age band of 65 years and above. According to the United States Census Bureau’s Population projections (2016) this number is anticipated to increase up to 20.59% in the year 2030 and up to 23.4% in the year 2060.
Table 1: The U.S. Population Projections (2016-2060)
| Age | Population | Percent Change | ||||||
| 2016 | 2020 | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | 2060 | 2016 | 2060 | |
| Less than 18 years | 73.6 | 74 | 75.7 | 77.1 | 78.2 | 80.1 | 22.78% | 19.8% |
| 18 to 44 years | 116 | 119.2 | 125 | 126.4 | 129.6 | 132.7 | 35.90% | 32.8% |
| 45 to 64 years | 84.3 | 83.4 | 81.3 | 89.1 | 95.4 | 97 | 26.09% | 24.0% |
| 65 years and over | 49.2 | 56.1 | 73.1 | 80.8 | 85.7 | 94.7 | 15.23% | 23.4% |
| Total | 73.6 | 74 | 75.7 | 77.1 | 78.2 | 80.1 | 22.78% | 19.8% |
Source: United States Census Bureau’s Population Projections, 2016 and DataHorizzon Research.
The ageing population negatively impacts a country’s economy as more people become dependents. In the year 2030, one out of five Americans is anticipated to be an older adult which further highlights the need to strengthen and improve the healthcare mechanism in the country. As a result, healthcare industry in the U.S. is anticipated to attract significant amount of investments, both from the state-federal funds and the private organizations over the next few years ensuring the steady growth rate.
Besides, it has been observed that digitalization has impacted the core functioning of the healthcare industry in the U.S. As consumers have become more aware of the services they need, the healthcare facilities have been forced to innovate their delivery models to ensure transparency and convenience at the same time maintain a balance in cost structures. Technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) have found their way into the industry operations and have helped deliver services as per the consumers’ expectations.
However, the industry does face some restraints in the U.S. The advanced medical equipment and other infrastructure facilities are considerably expensive, which may hinder the growth of the market. Furthermore, the industry faces a dire need of skilled individuals to cope up with increasing demands. The lack of skilled labor has resulted in significant rise in labor costs and increase in employee retention rates thereby burdening the companies with more operational costs. With increasing government investments in the form of incentives and subsidies, these factors are, however, anticipated to have a short-term impact on the healthcare industry.
U.S. Healthcare Industry and its segments
The healthcare industry in the U.S. can be broadly classified into segments as mentioned below:
- Medical equipment, devices and supplies
- Hospital services and facilities
- Medical insurance and managed care
- Pharmaceuticals
- Others
It has been observed that a citizen in the U.S. spends twice on healthcare as compared to people in other nations owing to highly expensive medical treatments and services. As a result, medical insurance and managed care segments of the healthcare industry enjoy a fair amount of dominance as opposed to the other segments.
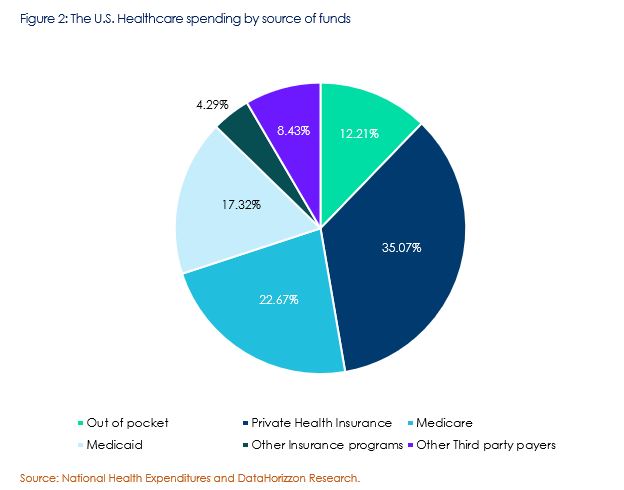
Majority of the healthcare spending is sponsored by private insurance companies in the U.S. accounting to as much as 35.07% of the total healthcare expenditure. Medicare and Medicaid the government sponsored medical insurance schemes acquire 22.67% and 17.32% respectively. With technological advancements and sophistication in diagnostics, the cost of healthcare services in the U.S. is anticipated to rise further which in turn is expected to fuel the demand of personalized private medical insurance products in the country over the next few years.
COVID-19 and its impact on the U.S.
Since the first COVID 19 case discovery in the U.S. in the month of January 2020, the total number of people suffering from the deadly virus as reached 5,54,849 as of April 12th 2020. The outbreak of this pandemic has resulted in approximately 21900 deaths across the nation which is the highest number of fatalities worldwide. With the rate of outbreak at its peak, the number of deaths is anticipated to be around 65,000-80,000 till the month of July 2020.
Some of the most affected states include New York, New Jersey, Michigan and California among others. The state of New York accounts to more than 1,90,000 cases with more than 10,000 deaths accounting to almost 50% of the entire death doll in the U.S. The total number of cases in the state have also surpassed the total cases in countries such as China, Italy and Spain among others. High population density, increasing number of commuters have been the primary reasons for such outbreak in the New York state.
Reluctance in implementing preventive measures, lack of government interference and awareness has resulted in rapid spread of the virus across major metropolitans in the U.S. Even if the situation is controlled fairly by the end of July 2020, spread of COVID 19 is expected to take a toll on the U.S. economically, psychologically and emotionally.
Table 2: Top 5 COVID 19 affected states in the U.S.
| Sr no. | State | Total Cases | Total Deaths |
| 1 | New York | 434,871 | 32,538 |
| 2 | California | 399,898 | 7,769 |
| 3 | Florida | 360,394 | 5,075 |
| 4 | Texas | 347,135 | 4,181 |
| 5 | New Jersey | 183,114 | 15,804 |
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and DataHorizzon Research.
Note: List as per the data on 19th July 2020.
COVID-19 and its impact on the U.S. Healthcare industry
The healthcare industry and its professionals including doctors, nurses and other support staff are the forerunners in the diagnosis and treatment of patients affected by COVID 19. With cases increasing exponentially, each day, in the U.S., the existing workforce has proved to be insufficient to attend the incoming number of patients. Furthermore, the healthcare industry has been facing the problem of lack of skilled labor historically. To cope up with this situation, a significant rise in employment has been observed with retired doctors and staff rejoining to fill in the void. Although, some of these employees have been signed on temporary basis by the hospital administration on daily wages, the operational costs have surged considerably.
Furthermore, in order to meet the shortage of hospital facilities and beds, the federal government has started converting stadiums, convention centers, and community halls among others into make shift hospitals. As a result, medical bed manufacturers are expected to face a sudden rise in the product demand positively impacting the business over the next few months. Moreover, hospital staff has been observed to be facing shortage of personal protection equipment (PPE), masks and ventilators among others. Imports of such peripherals has reduced significantly over the last 3 months owing to outbreaks and lockdowns in supplying countries. This shortage presents an opportunity for local and new players to enter the market and capitalize on the demand spike. The demand for ventilators, PPE and other medical peripherals is anticipated to be on the high at least for next 4-5 months.
COVID 19 has caused disruptions not in the U.S. but also worldwide. The U.S. imports variety of drugs and other raw materials from nations such China and India. Although China has showed signs of recovery, and is anticipated to get back on track by May 2020, India is still in the phase of lockdown which as hampered the supply of drugs and raw material to the U.S. The shortage caused by these disruptions have also resulted in increase of prices of these commodities.
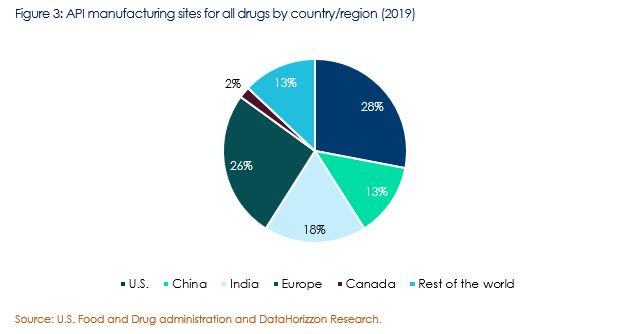
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the U.S. imports active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that are the actual drugs which are later formulated into injections, capsules and tablets, from various countries across the globe. Out of total API manufacturing industries supplying the U.S. market, only 28% were observed to be based locally, on the contrary as much as 72% of the API manufacturers were observed to be based overseas.
Moreover, supply of drugs such as ‘hydroxychloroquine’ that is used in combination with other drugs to cure COVID 19 is predominantly controlled by India which has set limitations on its export due to increasing number of cases in their country.
Massachusetts, New Jersey and California are known to be the hubs of pharmaceutical companies in the U.S. However, these states are also amongst the ones that have been affected the most. At the same time the demand for drugs and other pharmaceuticals has been at all time high owing to the increasing number of COVID 19 cases across the country. Although, pharmaceutical manufacturing has been classified as necessary and critical, the lockdown measures have significantly affected the supply chain of the companies, which as led to failure of these companies to match up with the demand. However, with such restrictions on imports of raw materials, the local pharmaceutical companies are anticipated to lessen their dependency on foreign suppliers and turn towards the local market players.
Short-Term impacts
- Increased demand for PPEs, masks, ventilators, ICU beds and other medical peripherals.
- Increased pharmaceutical sales
- Increased API imports in the U.S.
- Increased diagnostic kit imports.
- Rise in employment rate.
- Decrease in over-the-counter pharmaceutical sales.
- Decrease in heavy radiographic and other medical equipment sales
- Increase in handy medical device sales such as handheld digital thermometers, digital thermometers, digital blood pressure apparatus among others
Long-Term impacts
- Increased federal and private investments in development of preventive and curative vaccines, injections, drugs and tablets.
- Increased investment in hospital infrastructures and facilities.
- Overall increase in healthcare spending over the next 5-6 years.
- Increased investments in establishment of local raw material manufacturing units including pharmaceuticals, electronics and drugs.

